Intel HD Graphics (Skylake) vs Intel HD Graphics 4000 vs Intel HD Graphics (Bay Trail)
Intel HD Graphics (Skylake)
► remove from comparison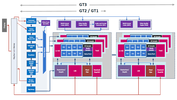
Die Intel HD Graphics (Skylake) (GT1) ist eine Prozessorgrafikkarte der im September 2015 vorgestellten Skylake-Generation. Für die meisten CPU wurden die Namen Intel HD Graphics 510 und Intel HD Graphics 515 genutzt.
Zwar glänzt die GPU mit einer extrem niedrigen Leistungsaufnahme, allerdings siedelt sich die Performance nur im untersten Low-End-Segment an und ist für neuere Spiele kaum ausreichend. Als sogenannte GT1-Ausbaustufe der Skylake-GPU verfügt die HD Graphics über 12 Execution Units (EUs), die je nach Modell mit bis zu 800 MHz takten.
Mangels eigenem Grafikspeicher oder eDRAM-Cache greift die HD Graphics (Skylake) über das Interface des Prozessors auf den System-RAM zu (2x 64 Bit DDR3L-1600/LPDDR3-1866).
Performance
Die exakte Leistung der HD Graphics hängt stark vom jeweiligen Endgerät und dessen TDP-Einstellung ab. Zum anderen bestimmt auch der eingesetzte Speicher die Performance.
Im Optimalfall dürfte die GPU in etwa mit der älteren HD Graphics 4200 konkurrieren und kann aktuelle Spiele (Stand 2015) nur in wenigen Ausnahmefällen flüssig darstellen.
Features
Der überarbeitete Videodecoder decodiert nun auch H.265-/HEVC-Videos vollständig in Hardware und arbeitet dadurch deutlich effizienter als bislang. Die Bildausgabe erfolgt über DP 1.2/eDP 1.3 (max. 3.840 x 2.160 @ 60 Hz), wohingegen HDMI nur in der älteren Version 1.4a angeboten wird. Ein HDMI-2.0-Anschluss kann aber mittels Konverter von DisplayPort ergänzt werden. Maximal lassen sich drei Displays parallel angesteuern.
Leistungsaufnahme
Die TDP des gesamten Chips liegt standardmäßig bei 6 Watt, sodass viele Ultrabooks oder 2-in-1-Geräte mit einer rein passiven Kühlung auskommen. Teils kann die TDP auch auf 4,5 Watt abgesenkt werden, wodurch allerdings die Performance sinkt.
Intel HD Graphics 4000
► remove from comparison
Die Intel HD Graphics 4000 (GT2) ist eine Prozessorgrafikkarte in den CPUs der Ivy Bridge Generation (3. Generation von Intel Core z.B. Core i7-3770). Je nach Prozessormodell wird die Intel HD Graphics 4000 unterschiedlich getaktet (und kann auf den unterschiedlich großen Cache zurückgreifen) und bietet daher eine teilweise deutlich geringe Leistung. Weiterhin kann die Taktung durch die Turbo Boost Technologie je nach Anforderung und TDP deutlich erhöht werden. In den schnellen Modellen soll der Basistakt 650 MHz und der Turbo 1.1 bis 1.25 GHz betragen. Die ULV Modelle weisen jedoch einen deutlich geringeren Basistakt auf (Sandy Bridge z.B. 350 MHz).
Im Vergleich zur HD Graphics 3000 der Sandy Bridge Prozessoren, bietet die 4000er einen eigenen Cache, überarbeitete DirectX 11 taugliche Shader (und vier mehr) und soll dadurch bis zu 60% mehr Leistung (3DMark Vantage) zeigen. Weiterhin sollte die GPU auf den gemeinsamen Last Level Cache (Level 3 Cache) des Prozessors zugreifen können. Weiters können die Shader auch für Direct Compute genutzt werden.
Erste Benchmarks positionieren die HD Graphics 4000 (in einem schnellen Desktop Quad-Core) auf dem Level einer Nvidia GeForce GT 330M und dadurch oberhalb der integrierten Prozessorgrafik Radeon HD 6620G. In unserem Unfangreichen Testbericht der HD Graphics 4000 konnte sie sich im schnellen Core i7-3820QM deutlich durchsetzen (6620G 15% langsamer). In den Mittelklassemodellen Core i7-3610QM und einem Dual-Core i5 war sie nur noch knapp schneller. Manchmal ist sogar eine langsame GeForce GT 630M in Reichweite. Gelegenheitsspieler, die bei Bedarf mit einer geringen Auflösung, deaktivierter Kantenglättung und niedrigen Settings leben können, werden daher an der HD Graphics 4000 durchaus Gefallen finden. In den ULV Prozessoren (Core ix-3xx7U) wird eine geringer getaktete Variante eingesetzt. Durch die TDP Beschränkungen kann der Turbo außerdem meistens nicht so hoch takten, wie bei den 35/45 Watt Versionen. Dadurch ist die HD Graphics 4000 hier meist etwa 30% langsamer als in schnellen Quad-Core CPUs.
Eine Besonderheit der Ivy Bride Grafikkerne ist, das nur 4x MSAA von der Hardware unterstützt wird. 2x MSAA wird per Software berechnet und geht durch die 4x MSAA Pipeline. Daher empfiehlt sich der Einsatz des gleich schnellen 4x MSAA.
Auch der integrierte Videodecoder genannt Multi Format Codec Engine (MFX) wurde kräftig überarbeitet und soll nun sogar mehrere 4K Videos parallel dekodieren können (ev nur in den High-End Modellen). DXVA Checker gibt weiterhin die Formate MPEG2, VC1, WMV9 und H264 als unterstütz an. QuickSync zum schnellen Transkodieren von Videos wurde ebenfalls verbessert und soll nun schneller bei gleichzeitig höherer Qualität laufen.
Ebenfalls neu ist die Unterstützung für drei unabhängige Bildschirme (abhängig von der Umsetzung im Notebook eventuell nur zwei gleichzeitige möglich). Bis jetzt waren nur zwei möglich und lediglich die AMD Grafikkarten mit Eyefinity Support bieten mehr als zwei Anschlüsse für Notebooks (jedoch nur mit DisplayPorts). Laut Intel wird DisplayPort in der Version 1.1 unterstützt (daher maximal 2560x1600) und HDMI in 1.4 (in der Praxis 1920x1080, siehe Fokusartikel für 2560x1600).
Der Stromverbrauch ist dank des 22nm Prozesses mit 3D Tri-Gate Technologie relativ gering und nicht einzeln angegeben. Die Notebook-Prozessoren (CPU, GPU, Speichercontroller) sind gesamt auf einen TDP von 18-45 Watt spezifziert.
Intel HD Graphics (Bay Trail)
► remove from comparison
Die Intel HD Graphics (Bay Trail) ist eine in den Tablet- (z.B. Z3770), Nettop- (z.B. J2850) und Notebook-SoCs (z.B. N3510) der Bay-Trail-Serie integrierte Grafikeinheit. Sie ist in verschiedenen Atom-, Celeron- und Pentium-Modellen zu finden und basiert auf der DirectX-11-tauglichen GPU der Ivy-Bridge-Generation. Taktrate und Einheitenzahl fallen allerdings deutlich niedriger aus, sodass sich die Performance nur im Low-End-Segment ansiedelt.
Im Vergleich zu Ivy Bridge, dessen Gen-7-GPU entweder 6 oder 16 Executions Units bietet, kommt die HD Graphics (Bay Trail) nur mit lediglich 4 EUs daher. Abhängig von Temperatur und Leistungsaufnahme kann die niedrige Basisfrequenz dynamisch bis auf den maximalen Turbo-Takt angehoben werden, der ja nach Modell bei bis zu 896 MHz liegt. Ebenfalls modellabhängig ist das Speicherinterface, welches im Single- oder Dual-Channel-Betrieb sowie mit verschiedene Speicherstandards (DDR3(L), DDR3L-RS, LPDDR3) arbeiten kann. Insbesondere Varianten mit einem nur 32 Bit breiten Interface (Atom Z3735G) verlieren teils erheblich an Performance.
Die schnellsten Notebook-Modelle erreichen knapp die Performance der HD Graphics (Sandy Bridge) sowie der Radeon HD 6310. Das reicht, um einige ältere und sehr anspruchslose Windows-Spiele wie World of Warcraft oder Half-Life 2 in niedrigen Einstellungen flüssig darzustellen. Für aktuelle Windows-Titel ist die GPU dagegen praktisch nicht geeignet.
Verglichen mit konkurrierenden ARM-SoCs ordnet sich die Grafikeinheit dagegen im unteren High-End-Segment ein und übertrifft knapp die Adreno 320, die in verschiedenen Qualcomm-SoCs wie dem Snapdragon 600 zu finden ist. Damit entspricht Grafik-Performance in etwa Nvidias Tegra 4. Auch sehr aufwändige Android-Spiele werden damit in hohen Auflösungen flüssig bewältigt (Stand 2013).
Der integrierte Videodecoder unterstützt alle gängigen Codecs wie MPEG2, H.264, VC1, MVC oder VP8 und ist für Auflösungen bis 4K (maximal 100 Mbit/s) geeignet. Das Bildsignal kann per HDMI 1.4 (max. 1.920 x 1.080) oder DisplayPort 1.2 (max. 2.560 x 1.600) an bis zu zwei Displays ausgegeben werden. Eine weitere Neuerung ist die Unterstützung von Wireless Display sowie Quick Sync, Intels schnellem und sparsamen H-264-Hardwareencoder. Einige dieser Features sind jedoch nicht bei allen Modellen verfügbar.
Je nach Modell liegt die Leistungsaufnahme des gesamten SoCs zwischen rund 2 und 10 Watt. Die besonders sparsamen Versionen sind damit auch für passiv gekühlte Tablets geeignet, andere werden in größeren (Sub-) Notebooks mit aktiver Kühlung eingesetzt.
| Intel HD Graphics (Skylake) | Intel HD Graphics 4000 | Intel HD Graphics (Bay Trail) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HD Graphics Serie |
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Codename | Skylake GT1 | Ivy Bridge | Bay Trail | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Architektur | Gen. 9 Skylake | Gen. 7 Ivy Bridge | Gen. 7 Ivy Bridge | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pipelines | 12 - unified | 16 - unified | 4 - unified | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kerntakt | 300 - 800 (Boost) MHz | 350 - 1350 (Boost) MHz | 311 - 896 (Boost) MHz | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speicherbandbreite | 64/128 Bit | 64/128 Bit | 32/64/128 Bit | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Speichertyp | DDR3L/LPDDR3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shared Memory | ja | ja | ja | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| API | DirectX 12_1, OpenGL 4.4 | DirectX 11, Shader 5.0, OpenGL 3.1 | DirectX 11, Shader 5.0, OpenGL 4.0, ES 3.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Herstellungsprozess | 14 nm | 22 nm | 22 nm | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Features | QuickSync | QuickSync | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Erscheinungsdatum | 01.09.2015 | 23.03.2011 | 11.09.2013 |
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


 Deutsch
Deutsch English
English Español
Español Français
Français Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Türkçe
Türkçe Svenska
Svenska Chinese
Chinese Magyar
Magyar